We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Know Your CHP Hand Tools
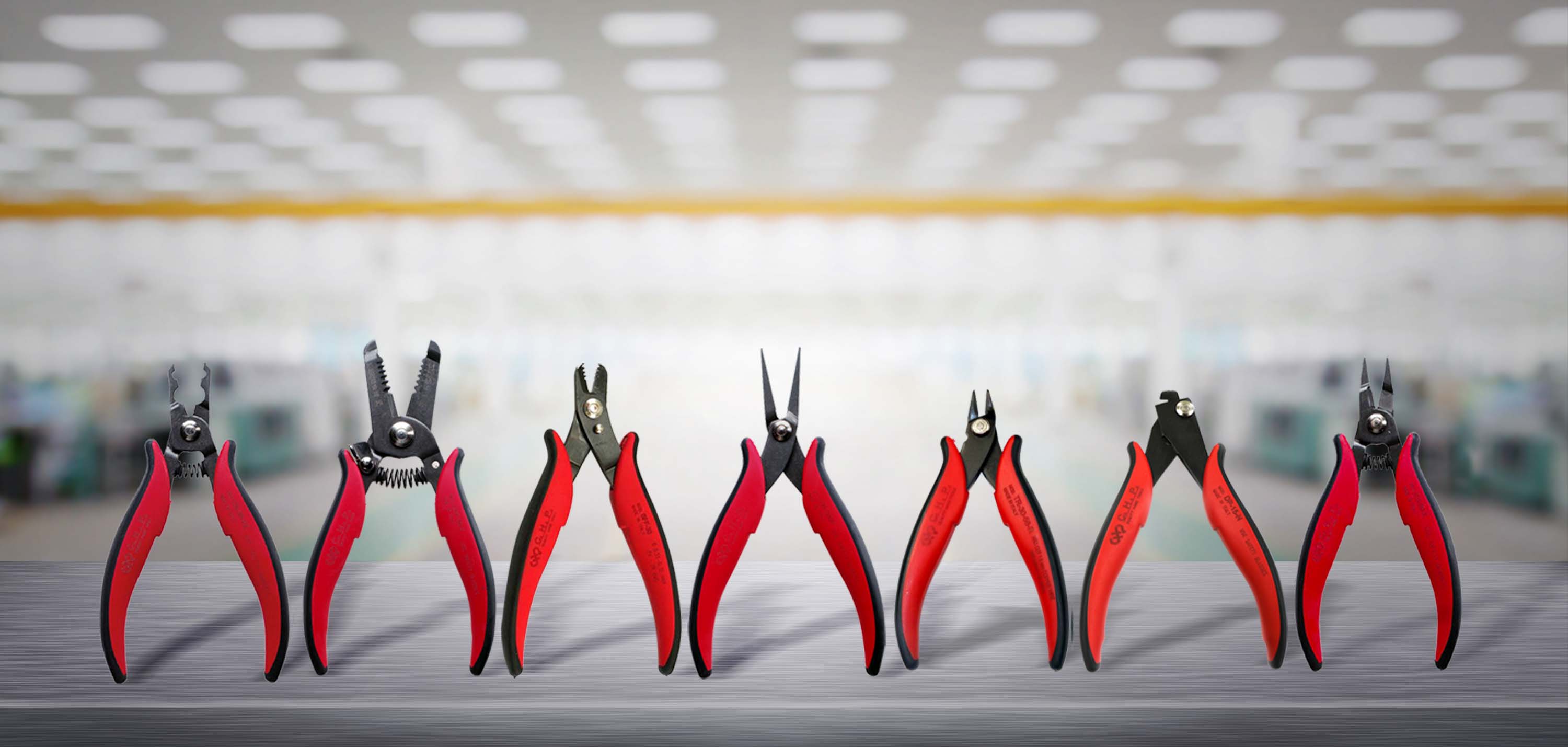

With so many hand-tool options, it can be difficult to know where to start or what to choose. There are cutters, shears, wire strippers, de-panelers, and pliers just to name a few. So how do you know what’s the right tool for your application?
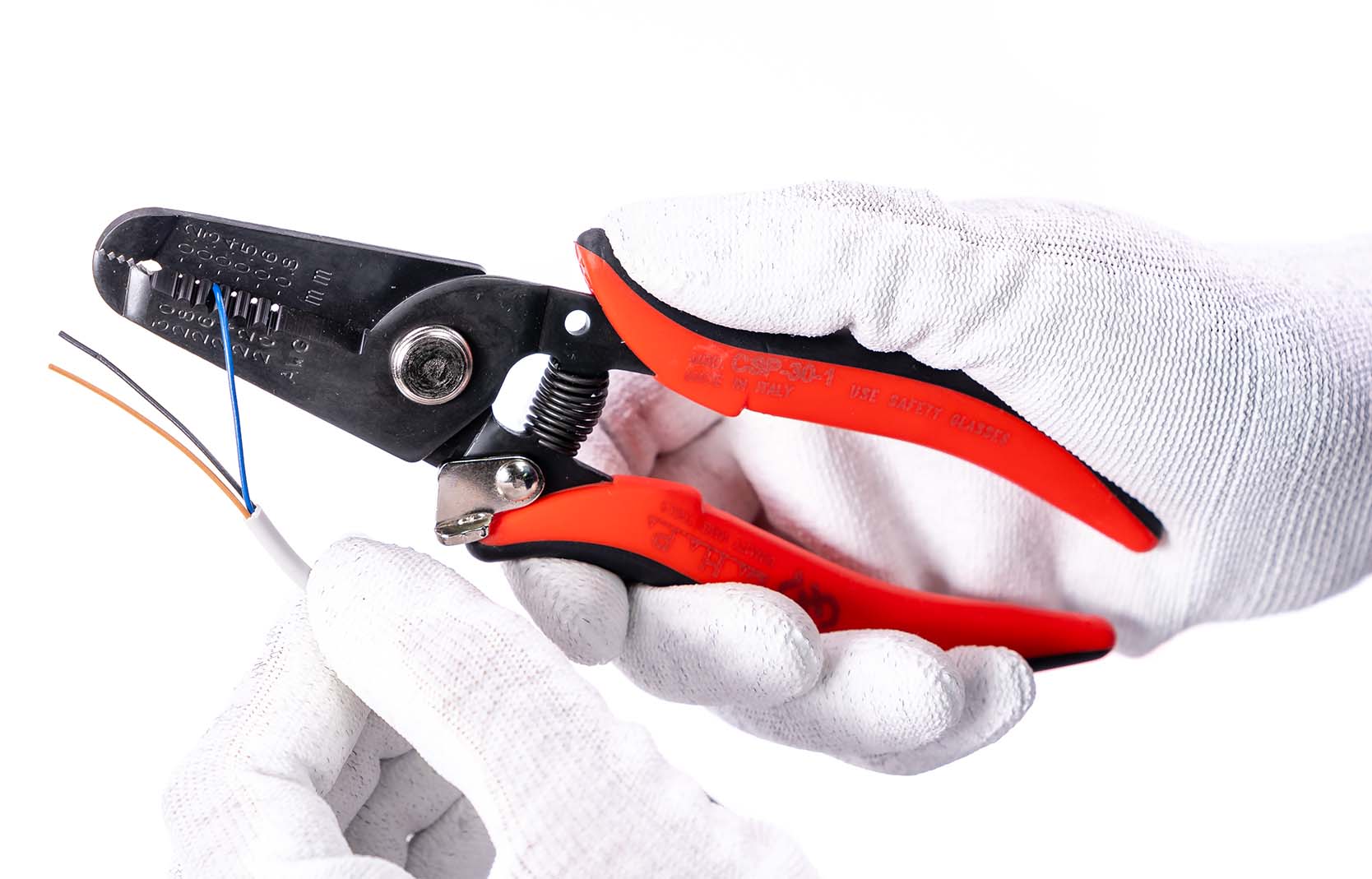
Before selecting a tool, you should consider, “what is the application and purpose I intend to use it for?” Are you looking to cut wire? Maybe grab and bend some leads? Maybe you are looking to strip insulation off of a wire? As we all know, each type of tool has its specific purpose. With the case of wire strippers, its purpose is to strip away the insulation material so that you have access to the inner conductors. When selecting the proper set of wire strippers, the most important factor you must consider, is the wire gauge, or AWG. If you’re unfamiliar with AWG (American Wire Gauge) just remember that the smaller the AWG number, the thicker/larger the wire is. The larger the AWG number, the smaller/finer the wire is. CHP wire strippers are available in various models depending on the wire gauge you are working with. Take for example, the CSP-30-1 model, which strips wire of 30-20 AWG; or the CSP-30-2 model which can strip wire 20-10 AWG. There are many other models to choose from depending on your application.
Pliers are primarily used for gripping, and/or bending of leads. The size and type of component will dictate the proper plier you would need as well as the type of nose you would likely use. The CHP series of pliers are available in various types as well, from long nose pliers (PN-2005) to short nose pliers (PN-2001), angled pliers (PNB-2005), and even specialty micro pliers (PN-20-M) for working on micro components in densely populated areas. There are also heavy-duty pliers made with thicker steel (5mm thick) for larger/heavier components and applications.

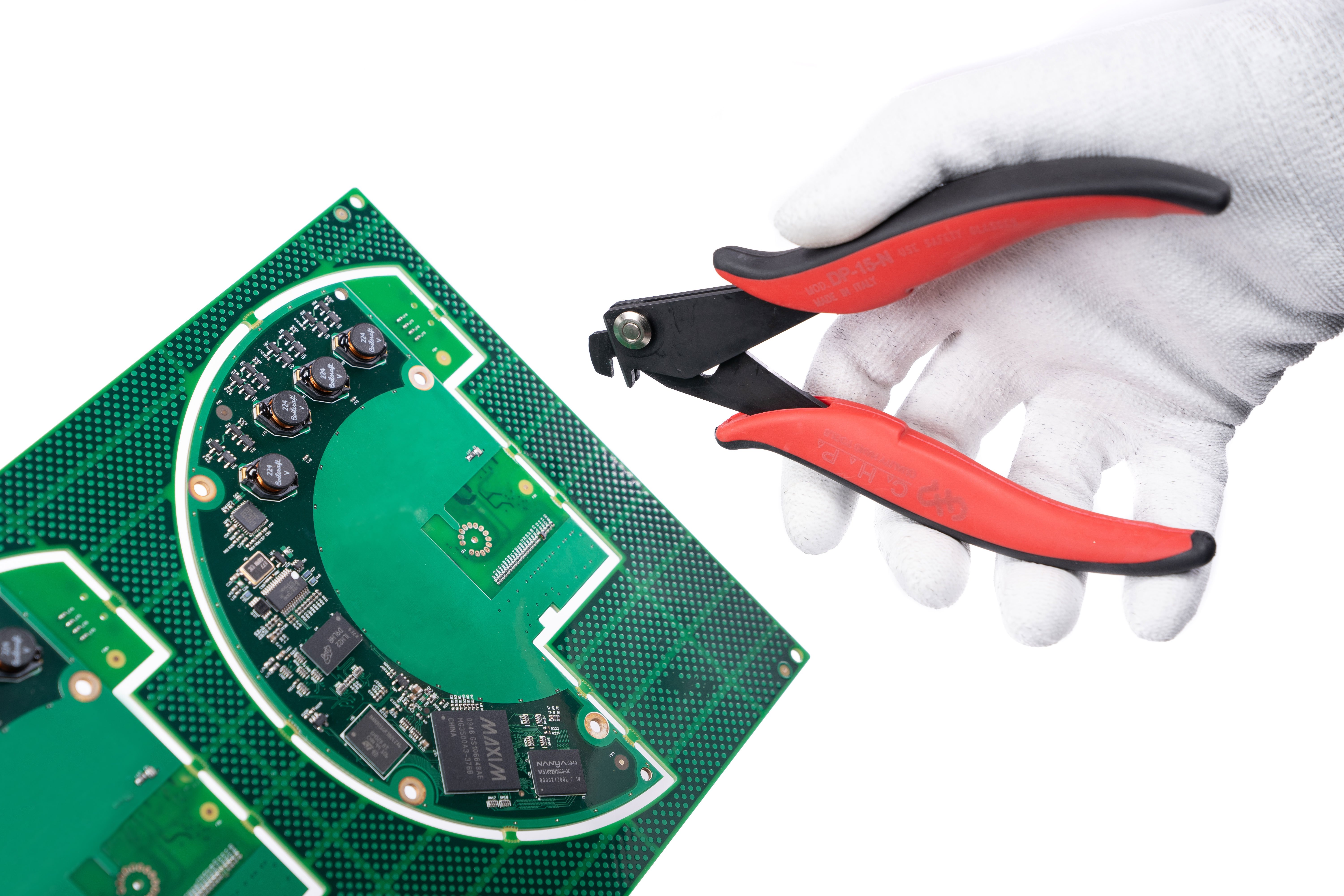
De-paneling tools are designed to remove PCB’s from multi-block circuit board panels. The important thing to consider when using de-paneling tools, is the thickness of the channel where the tab is located that you’ll be cutting and match it up with the thickness of the de-paneling tool head. For example, if the channel spacing is 1.5mm wide, you will use the DP-15-N tool, and for channels that are 2.0mm wide, you’d use the DP-20-N tool. There are also other sizes available, ranging from 1.5mm to 2.5mm in size.
Lead formers are suitable for the pre-forming or cutting of a wide range of component leads. To form a “C” shape standoff for axial and radial leads, you’d go with the PNR-30-D. There are also other types of lead formers that form AND cut off the leads as well, so it all depends on what you are looking for.
Out of the many CHP hand tools we have available, by far the most commonly used tool is the CHP Cutters. That is why there are so many options for cutters. To start with, there are four cutter types that the CHP line carries: Micro Cutters, Medium Cutters, Macro Cutters, and Standoff Cutters. Again, looking at the AWG size, and the material of wire will dictate which cutter type you would want to use. Micro is most used type with when working with smaller wire gauges, while the Macro type is used when working with the larger gauge wires.
An important factor to take into consideration is the type of cut you’re looking for. Cutters have a few different types of cuts with the 4 types that CHP carries being, Chamfered, Flush, Standoff, and Reverse. A chamfered cutter like the TR-5000 leaves the cut at an angle, while a flush cutter like the TR-5000-R will leave a clean cut. Standoff cutters such as the TR-5000-15 are used to cut component leads from 1.0mm to 14mm from the board surface. And a reverse cut simply has the cutting edge of the blade on the opposite side.
TR-5000
Chamfered Micro Cutters
TR-5000-R
Flush Micro Cutters
TR-5000-15
Standoff Cutter
| The following is a list to help you understand those indicators: | ||
| Indicator Codes | Descriptions | |
| T | Tungsten (ex. TRR-5000) the first ‘T’ indicates tungsten treated blades. | |
| Tungsten = High durability and wear resistance allow it to outperform steel tools where cuts are controllable and repeatable. | ||
| A | Safety clip (ex.TR-25-A) this is the TR-25 with a safety clip, without the “A” there is no safety clip. | |
| A safety clip applied to the blades protect the user from debris. | ||
| D | ESD safe dissipative handles (ex. CHP-170-D) | |
| Electrostatic Dissipative handles. Most of the CHP hand tools are also available with ESD handles. | ||
| SM | Small | |
| M | Medium | |
| G | Large | |
| L | Long (Handles are longer) | |
| P | Pointed (These have points to the blade) | |
| R | Special treated blades for cutting Ferrous materials. | |
| Ferrous = Material Containing Iron | ||
| PR | Specially treated blades with a point for cutting ferrous materials | |
You should consider these factors when choosing the right tool for your application. Once you know the specifics of the application, it will be easy to pick what tool will work best for you!
For additional information visit us at www.HakkoUSA.com or contact us at 1-800-88-HAKKO (42556) or at [email protected].
-HakkoUSA